May 10, 2022

The Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station's Rice Breeding Program off-season harvest in the U.S. territory of Puerto Rico pulled in a record amount of rice breeding materials this year for ongoing experiments and seed increases.
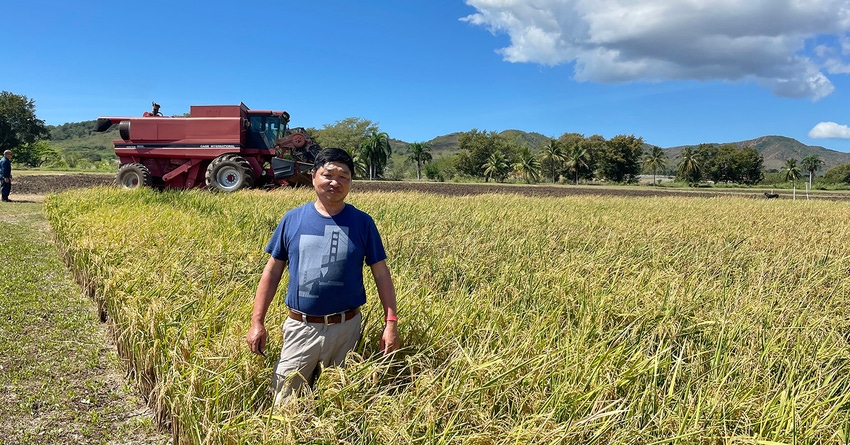
The rice research site at the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez’s Lajas Experiment Station has a long-running cooperative arrangement between the public breeding programs in Arkansas and other Mid-South states to decrease the number of years required to breed new lines of rice.
 The rice research site at the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez’s Lajas Experiment Station has a long-running cooperative arrangement between the public breeding programs in Arkansas and other Mid-South states to decrease the number of years required to breed new lines of rice. (U of A System Division of Ag)
The rice research site at the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez’s Lajas Experiment Station has a long-running cooperative arrangement between the public breeding programs in Arkansas and other Mid-South states to decrease the number of years required to breed new lines of rice. (U of A System Division of Ag)
Experimental varieties are first grown at the University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture’s Rice Research and Extension Center in Stuttgart. Seeds from chosen plants are grown in Puerto Rico during the winter. Seeds from the off-season harvest in Puerto Rico are then sent back to Arkansas in the spring to continue the breeding experiments, as well as produce additional seeds from new varieties for sale by the Arkansas Foundation Seed Program.
The Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station is the research arm of the Division of Agriculture.
Line development
Depending on differences between parental lines of a given rice plant cross, it takes seven to nine generations with rigorous selection to achieve the required uniformity and stability for a new variety to be ready for release, said Xueyan Sha, senior rice breeder for the experiment station. That process takes eight to 10 years if the progenies are only grown in Arkansas. The Puerto Rico nursery allows the breeding programs to shorten the development time by two to three years.
“Overall, we have had a very good off-season,” Sha said. “In addition to less COVID restrictions for travel and social distancing that limited a full crew, there has been a close-to-normal weather pattern in Puerto Rico from November to April and low disease pressure, especially rice blast.”
 Xueyan Sha, senior rice breeder for the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, works with the crew at the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez’s Lajas Experiment Station in March during the 2022 off-season rice harvest of breeding materials and seed increases. (U of A System Division of Ag)
Xueyan Sha, senior rice breeder for the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, works with the crew at the University of Puerto Rico-Mayaguez’s Lajas Experiment Station in March during the 2022 off-season rice harvest of breeding materials and seed increases. (U of A System Division of Ag)
Sha said they planted and harvested a record 5 acres of breeding materials and seed increases this off-season. About 6,000 pounds of rice seed have been shipped back for planting this year. The Arkansas Rice Breeding Program usually harvests and ships back about 1,000 pounds of seed each year for breeding and trials.
The increase in rice seed this year is primarily due to production of Ozark breeder seed, a long grain variety publicly released in January, Sha said. Seventy bags of Ozark breeder seed — seed used to grow the foundation or other classes of seed — were shipped from Puerto Rico to the Rice Research and Extension Center in Stuttgart to grow this year.
New lines
Sha said they also harvested purification plots for three potential Provisia® long grain lines at the Puerto Rico nursery, as well as seed purification and propagation plots of three new-and-improved male sterile lines for hybrid seed production this summer at the Stuttgart location. Sha noted that “purity” means the seed is authentic to the breeder’s description without other rice off-types or variants mixed in.
Sha said the off-season seed purification project included a promising conventional long grain line, which is bred to have resistance to blast, a fungal disease common in Arkansas. The potential future release has “excellent grain quality and showed a very good yield potential in the 2021 Arkansas Rice Performance Trial,” Sha added.
Arkansas rice researchers also used the Puerto Rico site to plant many second- and third-generation progenies of conventional Clearfield® and Provisia® long grain and medium grain test varieties for generation advancement, Sha added. Provisia® and Clearfield® are proprietary herbicide-resistant technologies.
New lines of rice are needed to further increase grain and milling yields, which improve production and the farmer’s financial bottom line, Sha said. New varieties are also bred to improve disease resistance to both existing and emerging diseases and other stresses like higher day and nighttime temperatures.
Source: University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture, which is solely responsible for the information provided and is wholly owned by the source. Informa Business Media and all its subsidiaries are not responsible for any of the content contained in this information asset.
You May Also Like