Lessons from state and local governments
Introduction
In June 2022, the most significant piece of gun violence prevention legislation in decades, the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, became law. Alongside several common-sense gun regulations, the law allocates $250 million for community-based violence prevention initiatives—a promising step toward promoting safety through non-carceral and community-centered approaches.1
This federal action is important, but it only scratches the surface of what can be done to keep communities safe from gun violence. From investing in youth employment programs to revitalizing vacant lots to improving the quality of neighborhood housing, a wealth of community-based safety interventions are proven to reduce violent crime—including gun violence—in the places most impacted by it, and tackle the conditions of inequality that allow violence to concentrate in the first place.2 But far too often, these community-based interventions are under-funded, particularly when compared to more punitive approaches.3
Luckily, another source of federal aid can fund community-based safety investments: the American Rescue Plan’s (ARP) $350 billion in Coronavirus State and Local Fiscal Recovery Funds. In addition to helping states and localities recover from the pandemic, the funds also provide local leaders with an unparalleled opportunity to address the public health crisis of gun violence. Indeed, President Joe Biden recently called on state and local leaders to use portions of this funding to address gun violence, including by “expanding evidence-based community violence intervention programs, and preventing crime by making our neighborhoods stronger with more educational and economic opportunities.”4
This research brief documents how state and local leaders are leveraging ARP funds to invest in non-carceral community-based safety initiatives; presents perspectives and case studies from leaders on-the-ground innovating on such strategies; and offers recommendations for how state and local leaders can maximize ARP funds to promote community safety prior to 2024 (when all funds must be obligated) and 2026 (when all funds must be spent). This is an unparalleled—and time-limited—window of opportunity, and states and localities should be thinking strategically right now about how to not only invest in proven strategies to reduce gun violence, but also promote life-affirming safety investments that support thriving communities.
Why non-carceral community-based investments are key for preventing gun violence
Despite news headlines to the contrary, the U.S. is not in the midst of a crime wave. But it is experiencing an unprecedented and alarming increase in murders, driven largely by gun homicides.5 Between 2019 and 2020, murder rates nationwide rose nearly 30%, while other forms of crime went down.6 Since then, homicides, gun assaults, and other forms of violent crime have continued to trend upward, and as of June 2022, the homicide rate was 39% higher than it was prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.7 For this reason, this brief focuses primarily on the role that community-based safety investments can play in addressing gun violence but it is important to note that these investments can also have broader impacts on public safety and community well-being.
To understand the effectiveness of community-based safety investments, it helps to look at where most gun violence occurs.8 Within cities and towns, gun violence is spatially concentrated—disproportionately occurring within a select set of high-poverty and disinvested neighborhoods, and within these neighborhoods, a select set of streets.9 These are also the places where indicators of structural disadvantage (such as poverty, racial segregation, lower educational attainment, and high unemployment) cluster.10 This pattern held during the recent nationwide increase in gun violence.11
The spatial concentration of violence stems from generations of policies and public and private investment decisions. Numerous studies have found a connection between state-sponsored racial segregation and gun violence, with the same places historically deemed unworthy of economic investment (through redlining) being more likely to be where gun violence concentrates today.12 Research has also identified a link between concentrated poverty, densely crowded housing, and vacant buildings with higher rates of violent crime, including gun homicides.13
Given the many place-based factors that contribute to gun violence, there is growing recognition that just like improving public health in other ways, reducing gun violence requires addressing its social determinants and looking outside traditional systems (such as courts or hospitals) to tackle its root causes.14 This approach is consistent with the preferences of survivors of violent crime, who overwhelmingly prefer investments in non-punitive crime prevention over criminal legal system responses.15 As the John Jay College of Criminal Justice recently pointed out, this approach is also consistent with an emerging and growing body of research that elevates the effectiveness of non-carceral public safety investments that put communities at the center and builds their capacity to advance safety, health, and economic opportunity.16
The next section of this brief examines four categories of non-carceral community safety investments that ARP funds are being used for. Before introducing examples of investments in each category, we provide further empirical justification for specific investments within that category. But while the empirical evidence matters, the underlying moral argument does as well: Mass incarceration is not a morally acceptable solution to systemic disinvestment.17 Local leaders should support non-carceral community safety interventions not only because they are effective, but because investing in struggling communities is the right thing to do.
Methodology
This brief pulls from public data state and local governments reported to the U.S. Treasury Department regarding ARP spending.18 We filtered projects by “Expense Category Group- 3-Services to Disproportionately Impacted Communities,” and further filtered by “Category-3.16-Social Determinants of Health: Community Violence Interventions.”19 These filters, which Treasury has since recategorized as “Category 1 Public Health, 1.11 Community Violence Intervention,” document instances in which state and local leaders are purposefully aiming to reduce violence by addressing social determinants. We recognize that there are many more projects that are not coded as violence interventions that can still have an outsized impact in reducing violence, such as those designed to restore vacant lots or pilot universal basic incomes. However, we believe it is important to highlight how states and localities are explicitly thinking about violence prevention through community-centered approaches.Within the Community Violence Intervention designation, we also filtered out funding allocated to victim services. While such projects are commendable and necessary, they are responses to violence, whereas our brief is concerned with interventions that prevent violence. Additionally, this brief focuses entirely on non-carceral safety uses of ARP funds, meaning we excluded uses that expand the reach of the criminal legal system (such as increasing the size of the police force or acquiring new public safety technology). The justification behind this approach is to highlight forward-looking and life-affirming visions of community safety, rather than carceral approaches that produce negative intergenerational consequences (such as mental health ramifications, family separation, poor educational performance, and racialized class stratification).20
Finally, we conducted qualitative interviews with 14 government and civic leaders working at the state, county, and city level.21 In selecting interviewees, we balanced attention to government and civil society and sought to center Black voices, particularly in localities with a large Black population.
How state and local leaders are leveraging ARP funds to invest in non-carceral safety strategies
While the most straightforward uses of the American Rescue Plan’s State and Local Fiscal Recovery Funds are to replace lost tax revenue or shore up general funds, the Treasury Department’s rules allow for a broad range of uses that “build a strong, resilient, and equitable recovery by making investments that support long-term growth and opportunity.”22 Treasury also makes clear that community safety interventions are valid expenditure types for all communities, particularly those that have suffered an uptick in violence.23 And as analysts at Civil Rights Corps, Alliance for Safety and Justice, the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, and other organizations have pointed out, these flexible funds offer the largest-ever influx of federal dollars to support states and localities advance non-carceral interventions that promote a holistic vision of community safety.24
Below is a curated list of state and local investments in non-carceral community safety interventions, categorized along four key dimensions of community well-being.25 While there are many more examples, our list represents a diverse set of locations with distinct approaches.
Enhancing economic opportunity to promote safety
A place’s economic health has a significant influence on its rates of violence; neighborhoods with higher poverty rates, unemployment, and income inequality have higher rates of violent crime.26 On the other side of this relationship, a promising body of evidence demonstrates that by enhancing economic opportunity and reducing inequality within neighborhoods, places can significantly reduce crime.27 For instance, evidence shows that youth workforce development and employment programs can reduce youth involvement in violent crime by as much as 45%.28 Improving school quality has also been found to reduce violent crime arrests.29 Finally, helping families avoid financial stress has been found to reduce crime and produce numerous other community benefits.30
Figure 1 illustrates how state and local governments are heeding this body of evidence and using ARP funds to advance community safety through economic mobility. For example, Illinois allocated $60 million investment toward youth employment programming, which subsidizes wages for high-risk youth and allows them to gain employability skills, participate in career development and apprenticeship programming, and receive wraparound services to address the root causes of employment barriers.
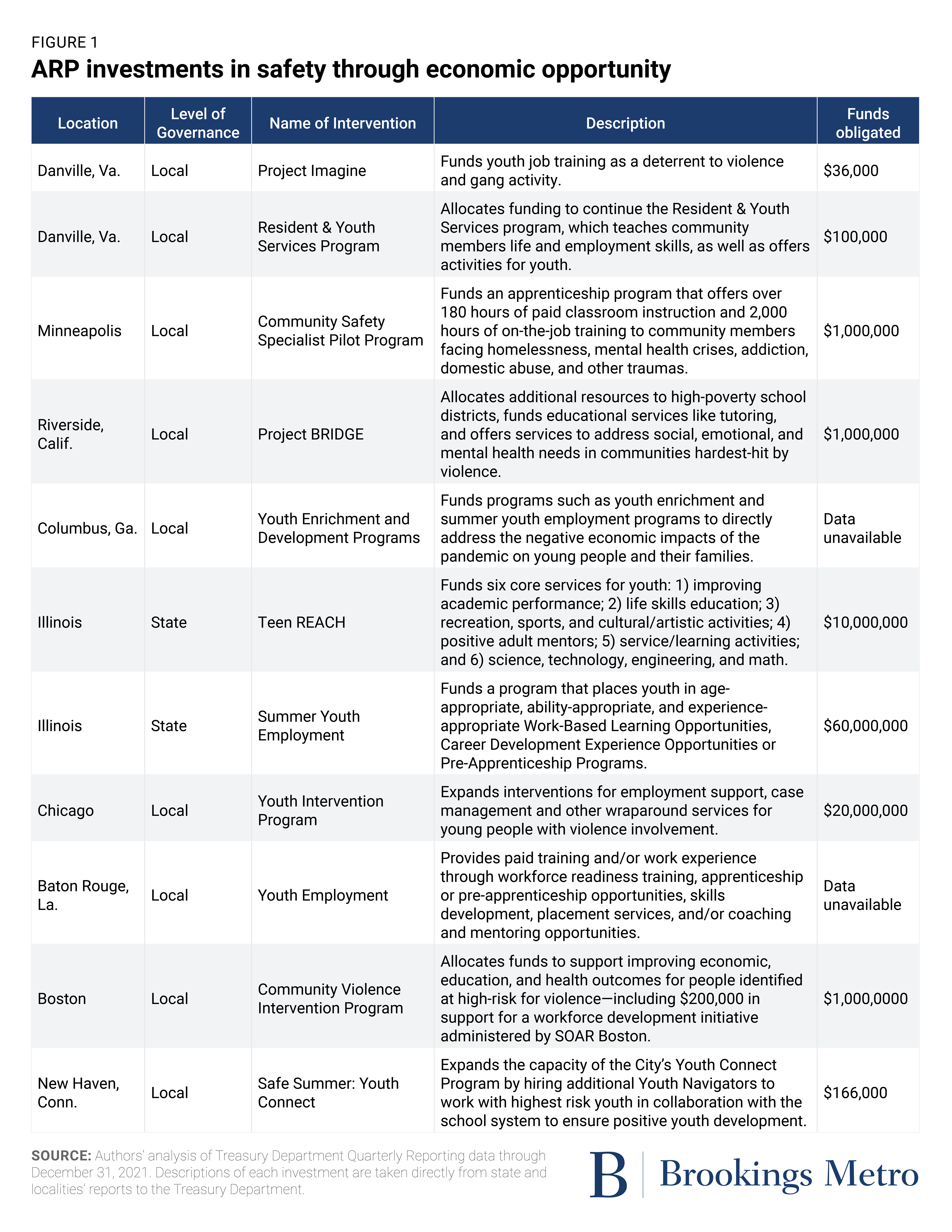
Case study: How a small city in Virginia is using ARP funds to reduce violent crime through youth workforce development
Danville is a Black-majority (49%) city in southern Virginia with a population of approximately 42,000. In 2016, it had the state’s highest per capita homicide rate, largely driven by gang-related violence. To tackle this, the city implemented a variety of community-centered programs to build trust in high-violence neighborhoods and prevent violence among at-risk youth. As Danville’s City Manager Ken Larking told us, “The best way to reduce crime is to prevent it and intervene before it happens.”
In 2020 (the year with the most recently reported data), Danville saw a 50% reduction in violent crime from 2016. The city’s focus on prevention is also central to how it’s using ARP funds. Larking said that Danville is allocating funds on both “direct” violence prevention (including $236,000 on community violence initiatives) as well as “indirect” violence prevention, such as $1 million to address blight and additional grants to help residents of disinvested neighborhoods start businesses.
Of particular note is Project Imagine, a youth workforce development and violence prevention initiative that received $36,000 in ARP funding. Project Imagine provides gang-involved or at-risk youth with mentorship, apprenticeships, and employment opportunities, and enables former participants to become “ambassadors” who represent their neighborhoods in city meetings and provide input on the city’s strategic plan.
“One thing I knew coming into this city is that there was no voice from the Black community that was being heard,” Robert David, who leads Project Imagine, told us. When David was brought on in 2018, he had no staff or budget, but was able to access unused city funds from the federal Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act to begin offering paid jobs to youth. He also turned everyday community spaces into hubs to promote workforce development. “We made the barbershop a haven,” he said, noting when one of his outreach workers isn’t there, people will ask the barber, “Where’s my man with the jobs?”
The infusion of ARP funds has helped David hire permanent outreach workers to connect with more youth, which has since significantly increased enrollment in the initiative. The funds have also enabled him to acquire a permanent building for Project Imagine, which will serve as a safe drop-in space and community center for youth.
Investing in the built environment and public health to promote safety
The most consistent evidence on the relationship between violence prevention and place exists in the realm of the built environment. Numerous studies find that the renovation of housing, vacant buildings, land, and lots as well as efforts to add greenery and improve air quality significantly reduce violent crime.31 These place-based strategies aim to counter decades of public and private disinvestment by revitalizing the physical environment and improving the health and safety of entire communities, rather than focusing on a sub-set of high-risk individuals (which many violence prevention programs, such violence interrupters, tend to focus on).32 These interventions also align with a public health approach to preventing violence, which addresses the environmental factors that increase susceptibility to violence and advances protective environments that nurture safety, health, and well-being.33 Examples range from addressing air pollution to increasing Medicaid coverage to expanding access to substance abuse and mental health treatment.34
Figure 2 highlights how state and local governments are using ARP funds to advance built environment improvements in communities and bolster public health system responses to community violence. For example, Chicago allocated ARP dollars to fund public realm improvements, building restorations, the preservation of safe and affordable housing, and the reactivation of city-owned land in the 15 areas with the highest rates of homicide and nonfatal shootings.
It is important to note that while Figure 2 includes built environment and public health interventions explicitly categorized as “community violence interventions,” there are many other examples of state and local governments investing in built environment improvements that have the potential to prevent violence and are not categorized as such. These include city beautification and a revitalized community park in Milwaukee, streetlight repair in Los Angeles, and weatherization efforts to remove lead and mold in Washington, D.C.35
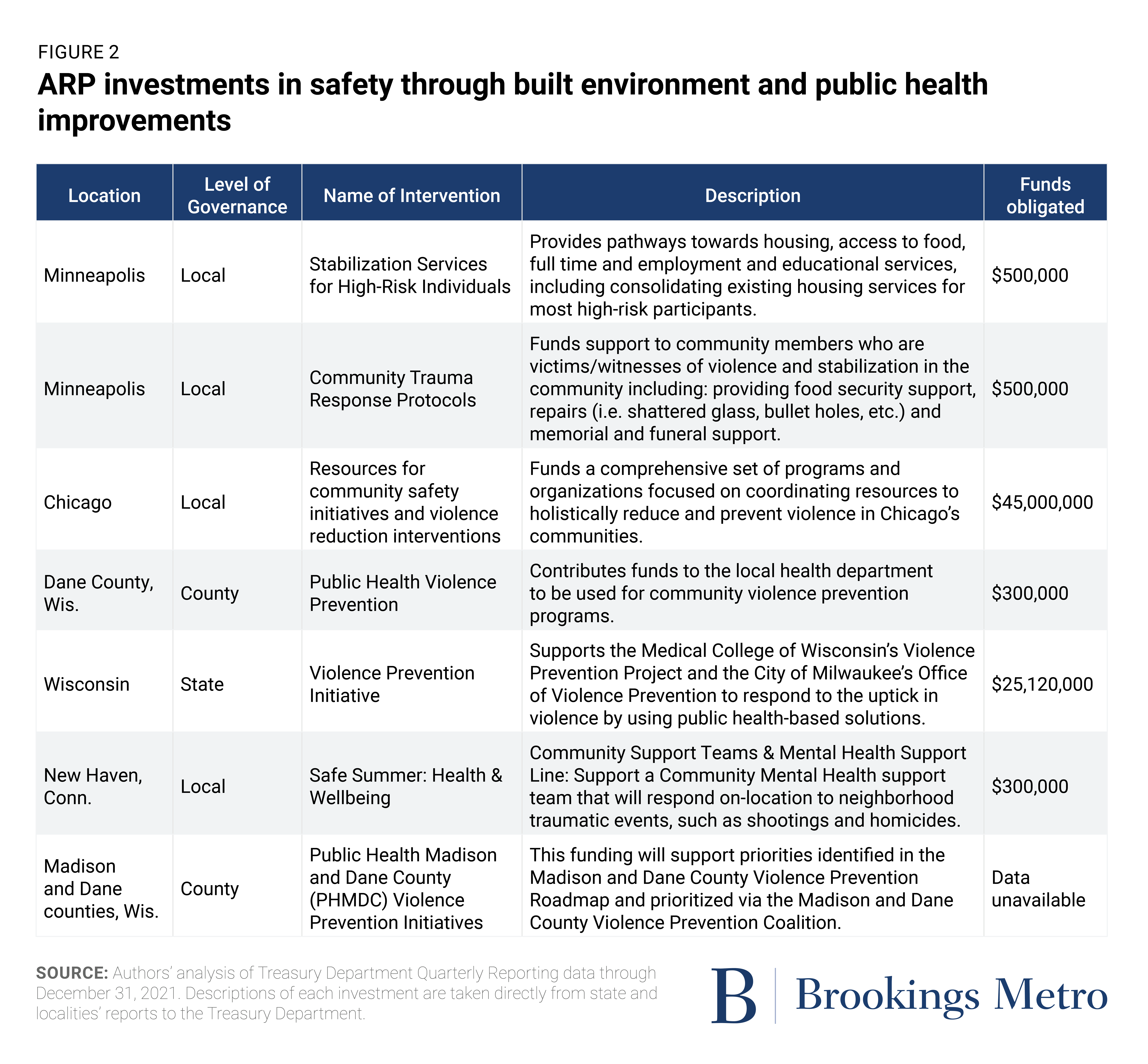
Case study: How Multnomah County, Ore. is taking a public health approach to violence prevention
Multnomah County is home to Portland, Oregon’s most populous city. During the pandemic, gun violence in the city nearly tripled. In response to this sharp uptick and an over-burdened social service system, county officials allocated over $61 million of their ARP funds to violence prevention, including $4 million in public health approaches.
“We drew a one-to-one connection between the uptick and gun violence and the pandemic,” said Adam Renon, senior policy advisor to the Multnomah County chair. “The loss of social cohesion, the isolation, the breakdown of traditional society norms. So, we said, let’s use ARP funds to address that.” The county allocated $300,000 to hire “community health specialists” who provide families directly impacted by gun violence with safety plans and trauma support. An additional $1.2 million went toward creating a behavioral health response team of clinicians and peers to serve youth and families affected by gun violence. And the county expanded existing programs, including the Habilitation, Empowerment, Accountability, Therapy (H.E.A.T.) curriculum—a cognitive behavioral therapy program meant to address generational traumas for justice-involved people.
Raffaele Timarchi, policy advisor to the county chair, explained the importance of embedding public health approaches to violence prevention across multiple county departments: “[Just because] we take a public health approach to violence prevention doesn’t mean that all of our investments have to be in a public health department…We want to spread the tools of public health into these other departments, including people working at the community level.” This approach ran through Multnomah County’s ARP safety allocations, which included significant investments to strengthen communities through emergency rental assistance, community organization incubators, and a $4.8 million investment in direct assistance to help pay for residents’ pressing financial needs, including food, child care, transportation, and living expenses
“We drew a one-to-one connection between the uptick and gun violence and the pandemic. The loss of social cohesion, the isolation, the breakdown of traditional society norms. So, we said, let’s use ARP funds to address that.”
Adam Renon, Senior Policy Advisor, Multnomah County
Nurturing social cohesion to promote safety
A significant body of evidence demonstrates that social cohesion and feelings of belonging to a neighborhood are associated with lower violent crime rates.36 Research has also found that increasing the number of spaces for informal contact between neighbors (e.g., parks, community centers) is linked to a greater sense of safety for people in urban areas.37 A growing body of evidence even indicates that creative placemaking can enhance community safety.38
The evidence linking social cohesion with reduced violence forms the basis for many evidence-based community violence intervention programs, such as Cure Violence or Advance Peace,39 which rely on community outreach to reach individuals in neighborhoods at the highest risk for violence.40 These violence interrupting programs have contributed to significant declines in violence in high-crime neighborhoods in Richmond, Calif., Stockton, Calif., Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., Chicago, Baltimore, and others.41
Figure 3 highlights how state and local governments are using ARP funds to either invest in community violence interruption programs or in activities and programs that promote social cohesion. For example, Elkhart, Ind. is using ARP dollars to host summer events with music and food, present talks by credible messengers (e.g., people who have formerly been involved with the criminal legal system and now work in violence prevention), distribute anti-gun-violence yard signs, and provide COVID-19 information. Cincinnati is funding the Save Our Youth: Kings & Queens program, in which at-risk teens participate in a three-month program involving field trips and speakers focusing on Black history.

Case study: How St. Louis is preventing violence by investing in safe youth spaces
St. Louis is a midsized city (45.7% Black) with a population of roughly 300,000. Even with a slight decline in 2021, St. Louis continues to have one of the highest homicide rates in the nation. In recent years, there has been growing recognition among city officials that to prevent violence, they must target its root causes—starting with offering resources to those who are most at-risk for committing and be victims of violence, including youth in disinvested neighborhoods.
“We have over 50 kids that have been shot since the beginning of this year,” said Wilford Pinkney Jr., director of the Mayor’s Office of Children, Youth, and Families. “Most of our car jackings and car thefts are all juveniles…There was no one engaging with them to determine what is happening, why they engaged in that behavior, and to try to deal with addressing it early on. We need to deal with that before we get to the point that they’re car jacking and shooting people.”
As part of its ARP allocation, St. Louis devoted $5.5 million to violence interruption initiatives. One is Safer Summer St. Louis, which funds youth- and grassroots-led organizations to plan pop-up events aimed at providing safe, community-building spaces. Jessica Meyers, director for the St. Louis Area Violence Prevention Commission, said that motivation for the program came from youth themselves: “We heard from the youth that they feel like they do not have access to their whole neighborhood. They do not have access to safe spaces in their neighborhood. The spaces that should be safe, like parks, aren’t safe because of gun violence or drug dealing or gang activity. Or the spaces that are safe—like a recreation center or a YMCA or a business—they don’t feel welcome in them, or they feel there are barriers, whether that’s a fee or transportation.” Safer Summer St. Louis seeks to tackle this by providing funding (up to $5,000 per event) to youth in neighborhoods most impacted by gun violence to host events like block parties, bike rides, fitness events, and other activities of their choosing.
Meyers said that while the program is based on evidence about what works to prevent violence, it is really about showing St. Louis youth that the city is invested in their future. “[Safer Summer St. Louis] is about investing in youth and telling them we value them enough that we’re taking this $1 million in [ARP] funding and we’re going to put it directly to events that allow you to be young and have fun in St. Louis—in a safer St. Louis.”
“[Safer Summer St. Louis] is about investing in youth and telling them we value them enough that we’re taking this $1 million in [ARP] funding and we’re going to put it directly to events that allow you to be young and have fun in St. Louis—in a safer St. Louis.”
Jessica Meyers, Director of the St. Louis Area Violence Prevention Commission
Strengthening civic infrastructure to promote safety
Nearly every non-carceral community-based safety intervention requires the leadership and dedication of civic and community-based organizations to be implemented.42 And aside from that, research indicates that the mere presence of such organizations within a neighborhood leads to reductions in violent crime.43 The challenge, however, is that while city resources are plentiful for increasing police in high-crime neighborhoods, cities routinely fail to fund the community infrastructure (such as grassroots organizations) that stabilize communities.44
Figure 4 highlights how state and local governments are using ARP funds to enhance the capacity of community-based and civic organizations to prevent violence. For example, New Haven, Conn. used $785,000 of its ARP funds to create Civic Space, a centralized public forum for citizens and grassroots organizations to share input on ARP investments, learn about new community-centered violence prevention initiatives, and partner with other organizations working on similar aims.
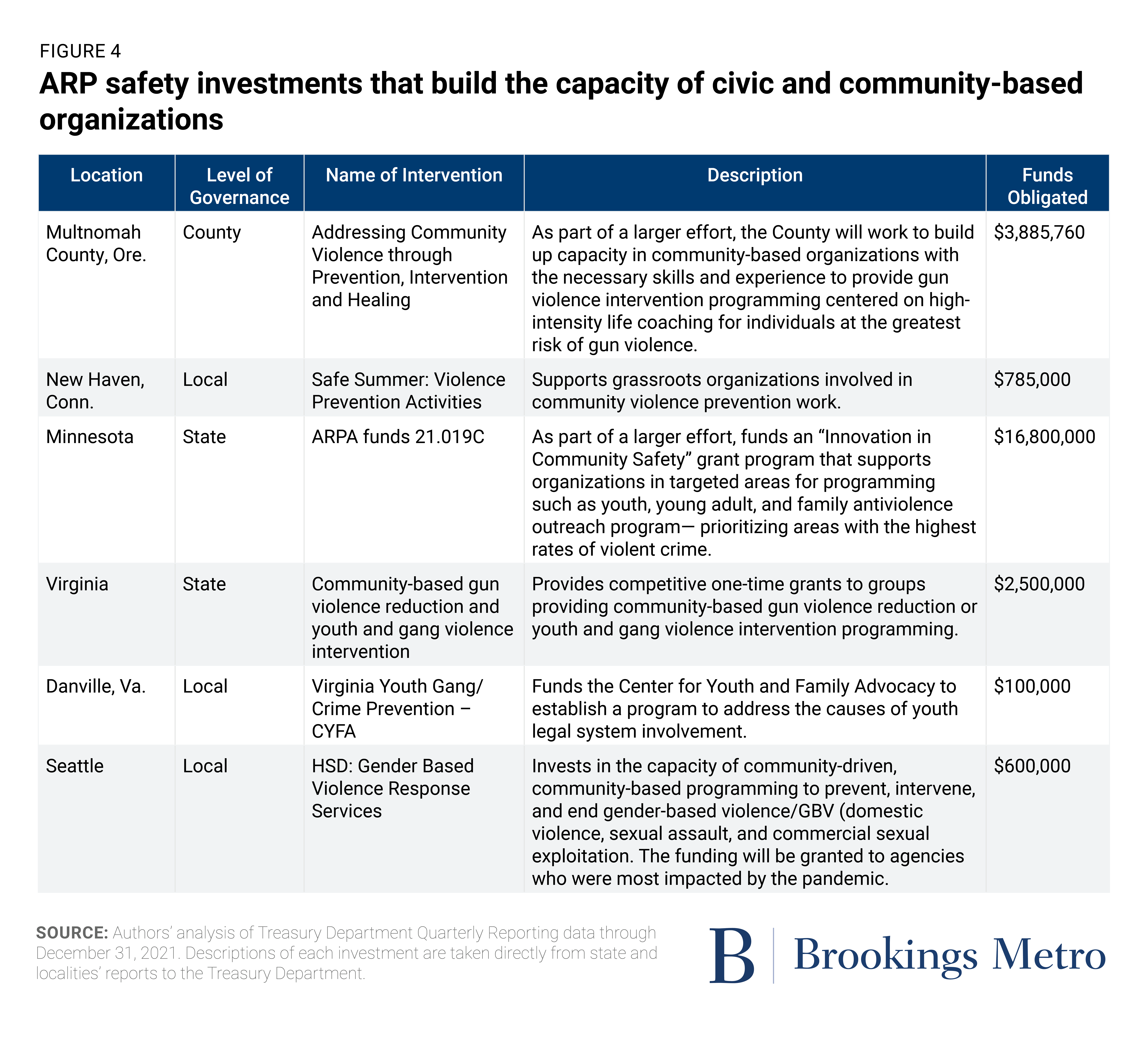
Case study: How Minnesota is supporting locally led grassroots organizations prevent violence
Minnesota has a population of 5.7 million, with the largest concentrations in the cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul. Despite relatively strong gun laws, firearms are the leading cause of death for youth in the state. With Minneapolis being the site of George Floyd’s murder and the catalyst for global protests against racial injustice, the state knew it needed to act boldly in allocating ARP funds toward non-carceral public safety approaches—ultimately obligating $16.8 million for violence prevention and intervention activities as well as survivor support.
As part of this, state leaders allocated $5 million toward a new Innovation in Community Safety grant program. Kate Weeks, executive director of the Minnesota Department of Public Safety, said the program is “a new way for Minnesota to push out money that was community-focused,” where “decisions about where funds would go come directly from the community.” The grant program provides local organizations in targeted neighborhoods with up to $1 million for community safety programming, prioritizing areas with the highest rates of violent crime. According to Weeks, the recipients have been “virtually all nonprofits.”
The state made another $2.5 million available through Violence Intervention Grants, with a maximum per-grant amount of $250,000. These grants were designed to have a more equitable distribution of applicants, with a fiscal agent administering smaller funding amounts more quickly to grassroots organizations.
Recommendations from the field: Maximizing ARP funds to promote holistic community safety
The state, county, and local leaders we interviewed offered five primary recommendations on how to more equitably and effectively allocate ARP spending toward non-carceral community safety interventions. These recommendations, which align with emerging research on best practices for the equitable use of ARP funds, include:
- Build the capacity of smaller, grassroots nonprofits to deploy funds. States and municipalities rely on nonprofit partners to execute ARP obligations; small and grassroots nonprofits (which often serve and hold greater trust with disinvested communities) are at a structural disadvantage in becoming aware of and applying for federal funds, as well as in navigating the reporting requirements tied to federal dollars.45 As Robert David explained, prior to Danville’s efforts to invest in violence prevention, there was a disconnect between grassroots organizations and “where the funding was,” which made the city “resource-rich but collaboratively poor.” Our interviewees explained how solving this mismatch requires direct outreach to nonprofits in disinvested communities to make them aware of ARP funds, simplifying the application process or dedicating state or municipal resources to support grassroots partners through the process, and loosening reporting requirements. For example, in St. Louis, the city hired a consultant to help grassroots nonprofits apply for funds. And in Minnesota, the state allocated different funding streams through a “social compact” model to allow some smaller nonprofits to pool their applications to make a stronger case for funding.
- Employ participatory and community-informed processes to guide investment decisions. To be true to the White House’s directive to use ARP funds equitably, disproportionately impacted communities should be engaged in determining how these federal dollars are spent. A variety of traditional mechanisms can be used to do so, including surveys, online forms, public meetings, and listening sessions. But these tools alone can often exclude citizens who are not already highly engaged or who have limited broadband access. Leaders must be intentional about diversifying the forms of community engagement and ensuring engagement is meaningful. Some strategies include targeted outreach in disadvantaged census tracts, using paid community reviewers (including youth) to review proposals and help make grantmaking decisions, conducting outreach to incarcerated and returning citizens, and launching longer-term processes such as participatory budgeting. For example, the St. Louis Area Violence Prevention Commission hired youth to review proposals for their Safer Summer St. Louis program, and Danville leveraged previous community engagement processes to guide the allocation of ARP funds. Stakeholders across all cities emphasized the importance of engaging youth.
“When we give power to young people to use their voice, to be able to co-create, that is more powerful than [when] we are just ordaining from on high and not letting them be effective partners,”
Devanshi Patel, CEO of the Center for Youth and Family Advocacy in Virginia.
- Prioritize equity in the allocation, implementation, and evaluation of ARP funds. The Treasury Department explicitly urged states and localities to prioritize equity in their distribution of ARP funds. In terms of funding allocations, equity can mean ensuring funding flows to census tracts with disproportionate rates of violence or to organizations whose leadership and staff are demographically representative of the communities they serve (for example, by requiring grant seekers to disclose this information in applications, as Minnesota did). In terms of implementation, interviewees explained that equity means trusting community-based organizations—particularly those with deep ties to underserved places—to use their funding in nimble ways that respond to communities’ evolving needs. Equity also means recognizing that people involved in implementation might not have standard resumes or may have criminal records, but their lived experiences and community ties are valuable assets for expanding the success and impact of these interventions. As Multnomah County’s Adam Renon told us, “We need to learn from the individuals who have been incarcerated or who have committed gun violence, and ask them, ‘What would have prevented you from entering that life?’” Finally, in terms of evaluation, equity means thinking expansively about compliance requirements and reporting metrics—including incorporating qualitative data and perspectives from directly impacted communities—as burdensome requirements can strain capacity and limit the ability of smaller organizations to access funding.
“We need to learn from the individuals who have been incarcerated or who have committed gun violence, and ask them, ‘What would have prevented you from entering that life?’”
Adam Renon, Senior Policy Advisor, Multnomah County
- Use data to not just understand program effectiveness, but to respond to evolving community needs. Upticks in violence can be unpredictable and send shockwaves across entire communities—disrupting school, family, and social life even for residents who may not have been directly victimized themselves. For this reason, interviewees stressed the importance of using public safety indicators not just to gauge whether prevention initiatives are working, but also as a way to shift implementation and resource allocation to respond to communities’ needs. “We really tried to take a look at the data in front of us,” Multnomah County’s Raffaele Timarchi said. “We knew that mental health concerns were up, we knew youth were disconnected from school and social supports…The safety net had been frayed.” Timarchi explained how the intersecting challenges of rising gun homicide rates, school closures, and frontline workers’ burnout guided their cross-disciplinary approach to violence prevention. Wilford Pinkney Jr. described using St. Louis’ crisis response data to craft programs that better fit community needs: “If you’re doing crisis response right, you’re engaging people and gathering a lot of data that’s hard for people to refute in terms of what the needs are in the community. We don’t have to guess what people need. We have 6,000 interactions from people in this community saying what they need.” Interviewees stressed this imperative to use data not as a way to judge high-violence communities, but rather as a tool to more deeply understand their shifting needs.
“If you’re doing crisis response right, you’re engaging people and gathering a lot of data that’s hard for people to refute in terms of what the needs are in the community. We don’t have to guess what people need. We have 6,000 interactions from people in this community saying what they need.”
Wilford Pinkney Jr., St. Louis
- Create dedicated and sustainable funding streams—including as line items in city budgets—and braid funding streams whenever possible to increase scale. ARP provides state and local leaders with a once-in-a-generation influx of funds, but it is time-limited. Multiple interviewees expressed their concern that too great a reliance on this one-time funding could lead to programmatic cliffs. They noted that creating line items in city, county, or state budgets, and/or creating permanent agencies devoted to community safety could provide stability in financing—especially since political cycles and new administrations can disrupt initiatives that lack permanency.46 Our Brookings colleagues have also suggested braiding or blending funding streams to increase sustainability, which could involve braiding ARP dollars with private funding, funding from surrounding regional jurisdictions, or major new federal investments like those in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. Finally, municipalities should harness revenue from traditional economic development initiatives to sustain public priorities. For example, Danville City Manager Ken Larking outlined a vision for current development that includes the goal of never being “in a budget crisis where a neighborhood park has to be sacrificed because there isn’t enough money to do police services or whatever else.” And as an added benefit, by tying revenue to priorities that reflect established city values and priorities, governments are held accountable to steering development that benefits the entire community.
Conclusion
At the end of 2021, cities and counties had budgeted only 40% of their total ARP allocation (82% of the first of two funding tranches). While more money has been budgeted this year, there is still plenty of funding left to be allocated prior to the 2024 deadline and spent prior to the 2026 deadline. It is vital that state and local leaders seize this once-in-a-generation opportunity to invest in community-based violence prevention efforts now, as these programs can take time to establish roots at the local level and scale up.
By investing in critical community safety infrastructure before the next rise in gun violence, communities will be better supported and equipped to avoid such violence, while also averting the intergenerational consequences that accompany punitive responses to it. As Devanshi Patel of Virginia’s Center for Youth and Family Advocacy said, it is imperative to invest in “restorative justice and community-based programming now to help kids stay out of the legal system” because system-involvement and incarceration can create harms for people and communities that are felt for generations.
Ultimately, the benefits of addressing the root causes of gun violence go far beyond the shots you don’t hear. In addition to the lives saved, the benefits can be seen in the children playing in parks, the youth finding employment, the sick accessing treatment, the entrepreneurs launching businesses, or neighbors hosting block parties. By investing in economic opportunity, bolstering social cohesion, upgrading the built environment, and strengthening neighborhoods’ civic ties, state and local leaders can create the conditions necessary for long-lasting individual and collective flourishing.
Acknowledgments:
The authors express their sincere gratitude to the state and local leaders who participated in research interviews to inform this piece: Gregory Baldwin, Thomas Carr, Robert David, Patrick Hogan, Tricia Hummel, Ken Larking, Jessica Meyers, Ahna Minge, Dr. Kiah E. Nyame, Devanshi Patel, Wilford Pinkney Jr., Adam Renon, Raffaele Timarchi, and Kathryn Weeks. The authors also thank the following experts for their review of various drafts of the research brief: Alan Berube, Jennifer S. Vey, and Eli Byerly-Duke (of Brookings Metro), Sam Washington and Thea Sebastian (of Civil Rights Corps), and Leah Sakala (of Alliance for Safety and Justice).
Endnotes
- “Non-carceral” safety interventions are those that exist outside of the formal criminal justice system, and are implemented by actors who are not part of the criminal justice system.
- Heller, S., Pollack, H. A., & Davis, J. M. (2017). The effects of summer jobs on youth violence. National Criminal Justice Reference Service, Office of Justice Programs.
South, E. C., MacDonald, J., & Reina, V. (2021). Association between structural housing repairs for low-income Homeowners and neighborhood crime. JAMA network open, 4(7), e2117067-e2117067.
South, E.C. (2021). Opinion: To combat gun violence, clean up the neighborhood. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/10/08/opinion/gun-violence-biden-philadelphia.html. - Cashin, S. (2021). Opinion: It’s time to dismantle America’s residential caste system. Politico Magazine. https://www.politico.com/news/magazine/2021/09/12/its-time-to-dismantle-americas-residential-caste-system-511150
- White House. FACT SHEET: President Biden Issues Call for State and Local Leaders to Dedicate More American Rescue Plan Funding to Make Our Communities Safer – And Deploy These Dollars Quickly | The White House
- Michaels, Samantha. (2021). What If Everything You Know About Murder Rates and Policing Is Wrong? Mother Jones.
- MacFarquhar, Neil. (2021). Murders Spiked in 2020 in Cities Across the United States. New York Times.
- Council on Criminal Justice (2022). Pandemic, Social Unrest, and Crime in U.S. Cities: Mid-Year 2022 Update
- Love, H. (2021). Want to reduce violence? Invest in place. Brookings Institution.
- Weisburd, D. (2015). The law of crime concentration and the criminology of place. Criminology, 53(2), 133-157.
- Beard, J., C. Morrison, Jacoby, S., Dong, B., Smith, R., Sims, C., and Weibe, D. (2017). Quantifying disparities in urban firearm violence by race and place in Philadelphia, PA: A Cartographic Study. American Journal of Public Health.
- Rowlands, D. & Love, H. (2022). Mapping gun violence: A closer look at the intersection between place and gun homicides in four cities. Brookings Institution.
- Light, M. T., & Thomas, J.T. (2019). Segregation and violence reconsidered: Do whites benefit from residential segregation? American Sociological Review, 84(4), 690-725.
Jacoby, S., Dong, B., Beard, J., Wiebe, D., and Morrison, C. (2018) The enduring impact of historical and structural racism on urban violence in Philadelphia. Social Science & Medicine 199: 87-95. - Light, M. T., & Thomas, J. T. (2019). Segregation and violence reconsidered: Do whites benefit from residential segregation?. American sociological review, 84(4), 690-725.
U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (n.d.). Neighborhoods and violent crime. https://www.huduser.gov/portal/periodicals/em/summer16/highlight2.html.
Kondo, M. C., Andreyeva, E., South, E. C., MacDonald, J. M., & Branas, C. C. (2018). Neighborhood interventions to reduce violence. Annual review of public health, 39(1), 253-271.
Branas, C. C., Rubin, D., & Guo, W. (2012). Vacant properties and violence in neighborhoods. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012. - U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (n.d.). Healthy People 2030. https://health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/social-determinants-health
- Jones, A. (2020). Reforms without Results: Why states should stop excluding violent offenses from criminal justice reforms. Prison Policy Initiative. https://www.prisonpolicy.org/reports/violence.html#victims
- Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center.
Janetta, J., Sakala, L., & Rejon, F. (2020). Federal investment in community-driven public safety. Urban Institute.
Sakala, L. and La Vigne, L. (2019). Community-driven models for safety and justice. Du Bois Review, 16:1 253–266. - Barr, Anthony. & Broady, Kristen. (2021) Dramatically increasing incarceration is the wrong response to the recent uptick in homicides and violent crime. The Brookings Institution. Retrieved December 4, 2021, from http://www.brookings.edu/blog/the-avenue/2021/11/02/dramatically-increasing-incarceration-is-the-wrong-response-to-the-recent-uptick-in-homicides-and-violent-crime/
- U.S. Department of the Treasury. https://home.treasury.gov/policy-issues/coronavirus/assistance-for-state-local-and-tribal-governments/state-and-local-fiscal-recovery-funds/recipient-compliance-and-reporting-responsibilities
- In July 2022, The U.S. Department of Treasury released a new batch of reporting that includes data through March 2022 and can be found here: Recipient Compliance and Reporting Responsibilities | U.S. Department of the Treasury
- Geller, A., Fagan, J., & Tyler, T. (2017). Police contact and mental health. Columbia Public Law Research Paper, (14-571).
Legewie, J., & Fagan, J. (2019). Aggressive policing and the educational performance of minority youth. American Sociological Review, 84(2), 220-247.
Soss, J., & Weaver, V. (2017). Police are our government: Politics, political science, and the policing of race–class subjugated communities. Annual Review of Political Science, 20(1), 565-591.
Underwood, E. & Krinsky, M.A. (2019). Millions of children lose their parents to incarceration. That doesn’t have to happen. The Appeal. https://theappeal.org/millions-of-children-lose-their-parents-to-incarceration-that-doesnt-have-to-happen/
Sakala, L., Harvell, S., & Thompson, C. (2018) Public investment in community-driven safety initiatives: Landscape study and key considerations. Urban Institute. - Our list of interviewees consisted of the following: From Danville, Va.: Gregory Baldwin (Director of Restorative Practices at Center for Youth and Family Advocacy), Robert David (Youth and Gang Violence Prevention Coordinator), Ken Larking (City Manager), and Devanshi Patel (Co-Founder and CEO at Center for Youth and Family Advocacy. From St. Louis: Jessica Meyers (Director, St. Louis Area Violence Prevention Commission) and Wilford Pinkney Jr. (Director, Mayor’s Office of Children, Youth, and Families). From Multnomah County, Ore: Adam Renon (Senior Policy Advisor for Multnomah County Chair Deborah Kafoury) and Raffaele Timarchi (Policy Advisor for Multnomah County Chair Deborah Kafoury). From Minnesota: Thomas Carr (Executive Budget Officer at Minnesota Management & Budget), Patrick Hogan (Director of Communications at Minnesota Management & Budget), Tricia Hummel (Assistant Director, Minnesota Office of Justice Programs), Ahna Minge (Assistant Commissioner for Budget Services and State Budget Director, Minnesota Management & Budget), and Kathryn Weeks (Executive Director, Minnesota Office of Budget Programs). From Rochester, N.Y.: Dr. Kiah E. Nyame (Coordinator, Rochester Office of Neighborhood Safety).
- Coronavirus State and Local Fiscal Recovery Funds | U.S. Department of the Treasury
- https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2022-01-27/pdf/2022-00292.pdf
- Civil Rights Corps. (n.d). Community safety & the American Rescue Plan: A guide to using fiscal recovery grants to advance holistic safety. https://civilrightscorps.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Community-Safety-and-ARP_Policy-Guide_CivRightsCorps.pdf,
Lazere, E. (2021). Using federal relief funds to invest in non-police approaches to public safety. Center on Budget and Policy Priorities.
Heuvel, S., Nelson, M., & Nguyen, L. (2021). How the American Rescue Plan can foster an equitable recovery: An equitable recovery requires strategic investments in safety. Vera Institute of Justice. - Love, H. (2021). Want to reduce violence? Invest in place. Brookings Institution.
- U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (n.d.). Neighborhoods and violent crime. https://www.huduser.gov/portal/periodicals/em/summer16/highlight2.html.
- Sebastian, T., Bou, L., & Washington, S. Getting Smart on Safety Evidence on Non-Carceral Investments That Work to Prevent Violence & Harm. Civil Rights Corps.
- Heller, S. B. (2014). Summer jobs reduce violence among disadvantaged youth. Science, 346(6214), 1219-1223.
- Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center.
- Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center.
- South, E. C., MacDonald, J., & Reina, V. (2021). Association between structural housing repairs for low-income Homeowners and neighborhood crime. JAMA network open, 4(7), e2117067-e2117067.
Branas, C. C., South, E., Kondo, M. C., Hohl, B. C., Bourgois, P., Wiebe, D. J., & MacDonald, J. M. (2018). Citywide cluster randomized trial to restore blighted vacant land and its effects on violence, crime, and fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(12), 2946-2951.
Kondo, M. C., South, E. C., Branas, C. C., Richmond, T. S., & Wiebe, D. J. (2017). The association between urban tree cover and gun assault: a case-control and case-crossover study. American journal of epidemiology, 186(3), 289-296.
Bondy, M., Roth, S., & Sager, L. (2020). Crime is in the air: The contemporaneous relationship between air pollution and crime. Journal of the Association of Environmental and Resource Economists, 7(3), 555-585. - Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center.
- American Public Health Association. (2018). Violence is a public health issue: Public health is essential to understanding and treating violence in the U.S. https://apha.org/policies-and-advocacy/public-health-policy-statements/policy-database/2019/01/28/violence-is-a-public-health-issue.
- Sebastian, T., Bou, L., & Washington, S. Getting Smart on Safety Evidence on Non-Carceral Investments That Work to Prevent Violence & Harm. Civil Rights Corps.
- Brookings Institution (2022). Interactive: Local government ARPA investment tracker. http://www.brookings.edu/interactives/arpa-investment-tracker/.
- Weisburd, D., White, C., & Wooditch, A. (2020). Does collective efficacy matter at the micro geographic level?: Findings from a study of street segments. The British Journal of Criminology, 60(4), 873-891.
Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center. - Sullivan, William C., Frances E. Kuo, and Stephen F. Depooter. “The fruit of urban nature: Vital neighborhood spaces.” Environment and behavior 36, no. 5 (2004): 678-700.
- Treskon, M., Esthappan, S., Okeke, C., & Vásquez-Noriega, C. (2018). Creative Placemaking and Community Safety: Synthesizing Cross-Cutting Themes. Urban Institute.
- Dholakia, N. & Gilbert, D. (2021). Community violence intervention programs, explained. Vera Institute of Justice. https://www.vera.org/community-violence-intervention-programs-explained?emci=1e33529c-0d38-ec11-9820-c896653b26c8&emdi=c5fd9ca1-1738-ec11-9820-c896653b26c8&ceid=954462.
Delgado, S. A., Alsabahi, L., Wolff, K., Alexander, N., Cobar, P., & Butts, J. A. (2021). Denormalizing violence: A series of reports from the John Jay College Evaluation of Cure Violence Programs in New York City.
Advance Peace (n.d.). Learning and Evaluation. https://www.advancepeace.org/about/learning-evaluation-impact/. - Branas, C., Buggs, S., Butts, J. A., Harvey, A., Kerrison, E. M., Meares, T., … & Webster, D. (2020). Reducing Violence Without Police: A Review of Research Evidence. John Jay College of Criminal Justice Research and Evaluation Center.
- Pearl, B. (2020). Beyond policing: Investing in offices of neighbourhood safety. Washington: Center for American Progress.
Rust, M., Calvert, S., & Elinson, Z. Murder in America: What makes cities safer. Wall Street Journal.
Corburn, J. & Fukutome, A. Advance Peace Stockton: 2018-2020 evaluation. Center for Global Healthy Cities. - Sakala, L., Harvell, S., Thompson, C. (2018) Public investment in community-driven safety initiatives: Landscape study and key considerations. Urban Institute.
- Sharkey, P., Torrats-Espinosa, G., & Takyar, D. (2017). Community and the crime decline: The causal effect of local nonprofits on violent crime. American Sociological Review, 82(6), 1214-1240.
Sharkey, P. (2018). Uneasy peace: The great crime decline, the renewal of city life, and the next war on violence. WW Norton & Company. - Holder, S., Akinnibi, F., Cannon, C. (2020). ‘We have not defunded anything’: Big cities boost police budgets, CityLab.
- Brachman, L. (2022). Nonprofits’ critical role in deploying federal investments: Observations from the Transforming Cities Lab. Brookings Institution.
- Pearl, B. (2020). Beyond Policing: Investing in Offices of Neighborhood Safety. Center for American Progress


