The severity of pregnant women infected by Covid-19 does not have a significant impact on the prognosis of newborns, according to a study.
The research team at Korea University Anam Hospital released the result of its study, “Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes in Pregnant Women with Coronavirus Disease 2019,” in the Journal of Korean Medical Science (JKMS) on Monday.
The research team analyzed the prognosis of newborns according to the severity of Covid-19 in 257 pregnant women hospitalized at 15 institutions due to infection from January 2020 to December 2021.
The median age of the 257 pregnant women was 34 years, and 26 women, or 10.12 percent, were 40 and older. One-hundred-and-twenty had their first child, 26.1 percent were at early-stage pregnancy with three months, 33.1 percent were at the middle stage with over six months, and 40.9 percent were at late-stage pregnancy.
More pregnant women were infected by Covid-19 in the late pregnancy than those hit by the pandemic in the early and middle pregnancy. Twenty-nine, or 11.3 percent, had one or more underlying diseases, and 19 (7.39%) had pregnancy complications.
Most of them were mild cases. However, nine (3.5 percent) were hospitalized in intensive care units and two (0.78 percent) needed ventilators.
The examination of the health status of pregnant women and newborns who gave birth during the study period showed that the severity of Covid-19 in pregnant women did not affect the health of newborns.
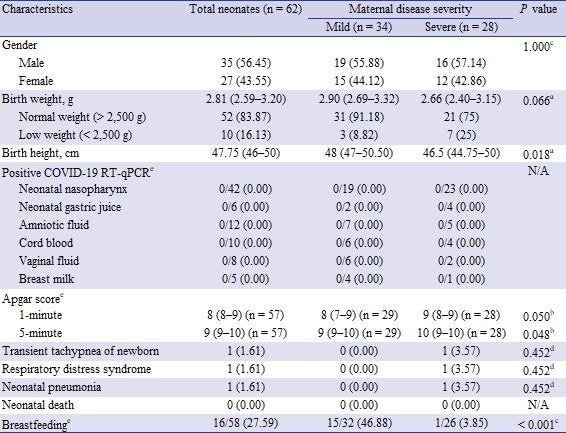
Sixty-five pregnant women gave birth, and 37 (56.9 percent) were mild Covid-19 patients and 28 (43.1 percent) were severe cases, according to the Covid-19 severity scale by the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
Fifty-one (78.5 percent) were delivered by Caesarean section, and all pregnant women with high severity of Covid-19 had a Caesarean. Five had an early amniotic wave, in which the amniotic fluid was rifled before the delivery began, and three miscarried.
Except for the three, 28 of the total 62 newborns, or 45.2 percent, were delivered by pregnant women with severe Covid-19, but vertical infections did not occur in all newborns.
Besides, newborns born by pregnant women who were severely ill showed higher Apgar scores than those born by mild patients. Apgar scores are clinical indicators of a baby's health condition shortly after birth, The higher the score, the healthier it is.
The investigation of the relationship between Covid-19 severity and pregnant women found that age and birth history at the time of Covid-19 infection were significant risk factors
“The childbirth results of pregnant women confirmed with Covid-19 were the same as those of uninfected pregnant women, and the possibility of vertical infection was extremely rare. However, you should be careful of pregnancy complications due to the severity of Covid-19," the study said. “A nationwide cohort study on the impact of Covid-19 on pregnant women is needed."
Although researchers collected data from 15 hospitals, there was a limitation to generalizing the result, as it contained small samples, the paper said. However, this study is significant as it was the first in Korea to investigate the relationship between pregnant women and newborns according to the severity of Covid-19.

